What is DDR?
DDR (Double Data Rate) is a type of computer memory that operates at twice the speed of its clock cycle, which enables it to transfer data at a higher rate than traditional SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory).
DDR memory allows for faster data transfer rates and improved system performance. There are several versions of DDR memory, including DDR, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4, with each version offering increased performance over the previous one. DDR memory is characterized by its clock speed, which is measured in MHz, and its memory bandwidth, which is measured in GB/s. DDR memory is commonly used in desktops, laptops, and servers, and its speed and performance are important factors to consider when building or upgrading a computer system. The amount of DDR memory needed depends on the type of tasks being performed and the requirements of the operating system and applications being used.
 0ms Transfer Rate
0ms Transfer Rate
 1080p
1080p
 10Gb SFP+
10Gb SFP+
 12V DC +-30%
12V DC +-30%
 1D Barcode
1D Barcode
 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz
2.4 GHz, 5 GHz
 2.5D Curved Glass
2.5D Curved Glass
 23AWG
23AWG
 2:1 Channel
2:1 Channel
 2D/3D Armrests
2D/3D Armrests
 3.5mm Port
3.5mm Port
 360 Degree Rotation
360 Degree Rotation
 3D
3D
 3D NAND
3D NAND
 3D Touch
3D Touch
 3G/4G
3G/4G
 4 SIP Lines
4 SIP Lines
 4-Pin PWM Fan Connector
4-Pin PWM Fan Connector
 4dBi Antenna Gain
4dBi Antenna Gain
 4K
4K
 4k/30fps
4k/30fps
 500cd/m2
500cd/m2
 5ATM
5ATM
 6.5mm Port
6.5mm Port
 60 ipm
60 ipm
 6DoF
6DoF
 6KV
6KV
 720p, 1080i, 1080p, 4K UHD, 8K UHD, HD
720p, 1080i, 1080p, 4K UHD, 8K UHD, HD
 8 Channel NVR
8 Channel NVR
 96dB
96dB
 A15 Bionic chip
A15 Bionic chip
 ABS Material
ABS Material
 Accelerometer
Accelerometer
 Access Point
Access Point
 Access Time Read
Access Time Read
 Access Time Write
Access Time Write
 Action Camera
Action Camera
 Active Area
Active Area
 Adaptive-Sync Technology
Adaptive-Sync Technology
 ADF
ADF
 AES Encryption
AES Encryption
 AH-IPS
AH-IPS
 AHD / HDCVI /HDTVI/CVBS
AHD / HDCVI /HDTVI/CVBS
 AIR CPU Cooler
AIR CPU Cooler
 Aluminum Alloy Material
Aluminum Alloy Material
 AM Frequency
AM Frequency
 AM/FM
AM/FM
 AMD Radeon
AMD Radeon
 AMD Radeon FreeSync
AMD Radeon FreeSync
 Ampere
Ampere
 AMVA
AMVA
 Animation
Animation
 Anti-Glare
Anti-Glare
 Antivirus
Antivirus
 Aperture
Aperture
 Architecture
Architecture
 ARDF
ARDF
 ARGB
ARGB
 Aspect Ratio
Aspect Ratio
 Audio Bit Rate
Audio Bit Rate
 Audio Compression
Audio Compression
 Audio Converter
Audio Converter
 Audio Encoding Format
Audio Encoding Format
 AutoCAD
AutoCAD
 Autofocus Assist Lamp
Autofocus Assist Lamp
 Call Log
Call Log
 Call Restriction
Call Restriction
 Call Waiting Caller ID
Call Waiting Caller ID
 Caller ID
Caller ID
 Camcorder
Camcorder
 Camera Lens
Camera Lens
 Carbon Fiber
Carbon Fiber
 Card Printer
Card Printer
 Cardioid
Cardioid
 Cartridge
Cartridge
 CAS Latency
CAS Latency
 Cash Register Machine
Cash Register Machine
 Cat-6 Keystone Jack
Cat-6 Keystone Jack
 Cat-6, Cat-7
Cat-6, Cat-7
 CCD Type
CCD Type
 Charging Efficiency
Charging Efficiency
 Cheque Scanner
Cheque Scanner
 Chipset
Chipset
 CIS
CIS
 Class 10 Speed
Class 10 Speed
 Clock Speed
Clock Speed
 CMOS
CMOS
 Coaxial Audio
Coaxial Audio
 Coaxial Cable
Coaxial Cable
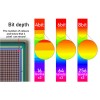 Color Bit / Bit Depth
Color Bit / Bit Depth
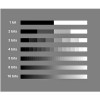 Color Bit Depth
Color Bit Depth
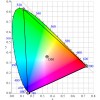 Color Gamut / Color Space
Color Gamut / Color Space
 Color Printer
Color Printer
 Color Reproduction
Color Reproduction
 Color Support / Display Color
Color Support / Display Color
 COM
COM
 Comb Spiral Binding
Comb Spiral Binding
 Commercial Display
Commercial Display
 Composite Video
Composite Video
 Condenser Microphone
Condenser Microphone
 Conductor Material
Conductor Material
 Conference Call
Conference Call
 ConferenceCam
ConferenceCam
 Contrast Ratio (TCR/DCR)
Contrast Ratio (TCR/DCR)
 Converter
Converter
 Copper Conductor
Copper Conductor
 Corded Phone Set
Corded Phone Set
 Cordless Phone Set
Cordless Phone Set
 CPU Cache
CPU Cache
 CPU Sockets
CPU Sockets
 Cross Cut
Cross Cut
 CrossFire
CrossFire
 CRT Monitors
CRT Monitors
 CUDA Core
CUDA Core
 Curved Screen
Curved Screen
 DADF
DADF
 Data Sync Compatibility
Data Sync Compatibility
 DDR
DDR
 Density 1U of Rack Server
Density 1U of Rack Server
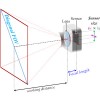 Diagonal Field of View
Diagonal Field of View
 Digital Broadcasting
Digital Broadcasting
 Digital Kiosk
Digital Kiosk
 Digital Noise Canceling
Digital Noise Canceling
 Digital Signage
Digital Signage
 Digital Voice Recorder
Digital Voice Recorder
 Digital Zoom
Digital Zoom
 Direct Thermal
Direct Thermal
 DirectX
DirectX
 Display Orientation
Display Orientation
 Display Port
Display Port
 Display Resolution
Display Resolution
 DLP
DLP
 DND Mode
DND Mode
 DNG
DNG
 DOC
DOC
 Document & Book Scanner
Document & Book Scanner
 Document Feeder
Document Feeder
 DOCX
DOCX
 Dolby Atmos
Dolby Atmos
 Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital
 Dolby/DTS
Dolby/DTS
 Dome CC Camera
Dome CC Camera
 DORI Distance
DORI Distance
 Dot Matrix Display
Dot Matrix Display
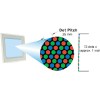 Dot Pitch
Dot Pitch
 Dotmatrix Printer
Dotmatrix Printer
 Double-Sided Card Printer
Double-Sided Card Printer
 Downstream
Downstream
 DPI
DPI
 Drive Bay
Drive Bay
 Driver Unit
Driver Unit
 Drone
Drone
 Drum Unit
Drum Unit
 DSLR
DSLR
 Dual Band
Dual Band
 Dual Port Headphone
Dual Port Headphone
 Dual Stereo Speakers
Dual Stereo Speakers
 Dual Stream Support
Dual Stream Support
 Duplex Print
Duplex Print
 Duplex Scan
Duplex Scan
 Dustproof
Dustproof
 Duty Cycle
Duty Cycle
 DVI
DVI
 DVI Converter
DVI Converter
 DVR
DVR
 DyAc Technology
DyAc Technology
 Dynamic Normalizer
Dynamic Normalizer
 E-PON
E-PON
 Earbuds
Earbuds
 Earmuffs
Earmuffs
 Earphone
Earphone
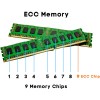 ECC Memory
ECC Memory
 ECC Support
ECC Support
 Efficiency of Power Supply
Efficiency of Power Supply
 Electrical Heart Sensor (ECG App)
Electrical Heart Sensor (ECG App)
 Elgato
Elgato
 ENERGY STAR Certified
ENERGY STAR Certified
 Engine Clock
Engine Clock
 EPEAT Level
EPEAT Level
 EPEAT Qualified
EPEAT Qualified
 EPS Connectors
EPS Connectors
 Ergonomic Design
Ergonomic Design
 Expansion Slots of Casing
Expansion Slots of Casing
 Exposure Compensation
Exposure Compensation
 Extension Cable
Extension Cable
 F1.8
F1.8
 Face Detection
Face Detection
 Face Plate
Face Plate
 Fast IPS
Fast IPS
 Fast VA
Fast VA
 Fax Machine
Fax Machine
 Female Port
Female Port
 FFS
FFS
 Fingerprint
Fingerprint
 Fireproof
Fireproof
 FireWire
FireWire
 Firmware
Firmware
 First Page Print
First Page Print
 Flash Memory
Flash Memory
 Flash Trigger
Flash Trigger
 Flash Type
Flash Type
 Flatbed Scanner
Flatbed Scanner
 Flicker-Free
Flicker-Free
 Flight Ceiling
Flight Ceiling
 Fluid Dynamic Bearing (FDB) of Fan
Fluid Dynamic Bearing (FDB) of Fan
 FM Frequency
FM Frequency
 Foam Type Cold-Cure
Foam Type Cold-Cure
 Focal Length
Focal Length
 Focal Length Ranges
Focal Length Ranges
 Form Factor
Form Factor
 Foveated Rendering
Foveated Rendering
 FPS
FPS
 Free-Angle Tilting Touchscreen LCD
Free-Angle Tilting Touchscreen LCD
 Frequency Response (Hz-kHz)
Frequency Response (Hz-kHz)
 Fully Modular & Semi-Modular Power Supply
Fully Modular & Semi-Modular Power Supply
 IC Configuration
IC Configuration
 ICR (Day & Night)
ICR (Day & Night)
 IEEE 802.11 b, g, n
IEEE 802.11 b, g, n
 IEEE 802.3i, 3u, 3ab, 3x
IEEE 802.3i, 3u, 3ab, 3x
 Impedance (ohm)
Impedance (ohm)
 Incoming Bandwidth
Incoming Bandwidth
 Ink Printer
Ink Printer
 Ink Printing Technology
Ink Printing Technology
 Ink Tank Printer
Ink Tank Printer
 Inkjet Coated Paper
Inkjet Coated Paper
 Input Frequency Range
Input Frequency Range
 Input Tray
Input Tray
 Insertion/Removal Cycles
Insertion/Removal Cycles
 Instant Gameview
Instant Gameview
 Interactive Board
Interactive Board
 Interactive Panel
Interactive Panel
 Interface
Interface
 Internet Security
Internet Security
 IP Camera
IP Camera
 IP Phone
IP Phone
 IP67
IP67
 IP68
IP68
 IPS
IPS
 IPS Panel
IPS Panel
 IR Range
IR Range
 ISO
ISO
 Label Printer
Label Printer
 Label Roll
Label Roll
 Laminating Speed
Laminating Speed
 Laminator Machine
Laminator Machine
 LAN
LAN
 Lan Card
Lan Card
 LAN Port
LAN Port
 Landscape
Landscape
 Large Format Printer
Large Format Printer
 Laser Printer
Laser Printer
 Laser Printing Technology
Laser Printing Technology
 LED
LED
 Lens Filter
Lens Filter
 Lens Hood
Lens Hood
 Lens Mount
Lens Mount
 Life Expectation
Life Expectation
 Light Life
Light Life
 Light Source (Watt)
Light Source (Watt)
 Light Source Life Hours (Economy)
Light Source Life Hours (Economy)
 Light Source Life Hours (Normal)
Light Source Life Hours (Normal)
 Light Source Type
Light Source Type
 Lightning Port
Lightning Port
 Linux
Linux
 Liquid CPU Cooler
Liquid CPU Cooler
 Lithium-Ion Polymer (LiPo)
Lithium-Ion Polymer (LiPo)
 Live View
Live View
 Loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
 LR6 Battery
LR6 Battery
 LTE FDD
LTE FDD
 Lumens
Lumens
 M.2
M.2
 Magic Clone Pano Panorama
Magic Clone Pano Panorama
 Magnet Proof
Magnet Proof
 Maintenance Box
Maintenance Box
 Male Port
Male Port
 Managed Network Switch
Managed Network Switch
 Manual Focus
Manual Focus
 Max Bitrate
Max Bitrate
 Max. Paper Size Custom
Max. Paper Size Custom
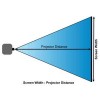 Max. Projection Distance
Max. Projection Distance
 Maximum Ascent Speed
Maximum Ascent Speed
 Maximum Descent Speed
Maximum Descent Speed
 Mechanic Wheel
Mechanic Wheel
 Mechanical Keyboard
Mechanical Keyboard
 Media Converter
Media Converter
 Memory Bandwidth
Memory Bandwidth
 Memory Bus
Memory Bus
 Memory Clock
Memory Clock
 Memory Components
Memory Components
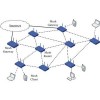 Mesh Technology
Mesh Technology
 Metal Detector
Metal Detector
 Micro HDMI
Micro HDMI
 Micro-USB
Micro-USB
 MicroSD UHS-I
MicroSD UHS-I
 Military-Grade Protection
Military-Grade Protection
 MIMO Technology
MIMO Technology
 Min. Projection Distance
Min. Projection Distance
 Mini DisplayPort
Mini DisplayPort
 Mini Tower, Mid Tower, and Full Tower Casing
Mini Tower, Mid Tower, and Full Tower Casing
 Mini UPS
Mini UPS
 Mini USB
Mini USB
 Mirrorless
Mirrorless
 Mobile Device Printing
Mobile Device Printing
 Modem
Modem
 Monaural Speaker
Monaural Speaker
 Money Counting Machine
Money Counting Machine
 Monochrome Bit Depth
Monochrome Bit Depth
 Monochrome Printer
Monochrome Printer
 Monthly Print Capacity
Monthly Print Capacity
 Motion Detection
Motion Detection
 MPEG-4
MPEG-4
 MTBF
MTBF
 MTTF
MTTF
 MU-MIMO
MU-MIMO
 Multi Function Printer
Multi Function Printer
 Multiple Copy
Multiple Copy
 Multitasking Supported
Multitasking Supported
 MVA
MVA
 Nano IPS
Nano IPS
 NAS Enclosure
NAS Enclosure
 Navigation Key
Navigation Key
 NCQ Support
NCQ Support
 Near Field Communications (NFC)
Near Field Communications (NFC)
 Neckband
Neckband
 Needle Threader
Needle Threader
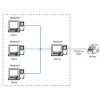 Network Protocol of Printer
Network Protocol of Printer
 Network Storage
Network Storage
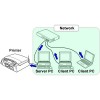 Networking of Printer
Networking of Printer
 NFC
NFC
 Ni-MH Battery
Ni-MH Battery
 Nibs
Nibs
 Nickel Plated
Nickel Plated
 Noise Cancelling Mic
Noise Cancelling Mic
 Noise Level of Power Supply
Noise Level of Power Supply
 Noise Reduction
Noise Reduction
 Non-Tangling Wire
Non-Tangling Wire
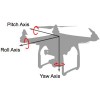 Number of Axes
Number of Axes
 Number of Diaphragm
Number of Diaphragm
 Number of Focus Points
Number of Focus Points
 Number of phone Line
Number of phone Line
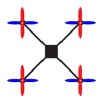 Number of Rotors
Number of Rotors
 NVMe
NVMe
 NVR
NVR
 OCR
OCR
 OCR Languages
OCR Languages
 Octa-Core/Hexa-Core/Quad-Core
Octa-Core/Hexa-Core/Quad-Core
 OLED Display
OLED Display
 OLT
OLT
 Omnidirectional Microphone
Omnidirectional Microphone
 OpenGL
OpenGL
 Operating Humidity
Operating Humidity
 Operating System
Operating System
 Operating Temperature
Operating Temperature
 OPS
OPS
 Optane Memory
Optane Memory
 Optic Elements
Optic Elements
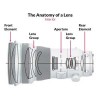 Optic Groups
Optic Groups
 Optical Heart Sensor
Optical Heart Sensor
 Optical Image Stabilizer (OIS)
Optical Image Stabilizer (OIS)
 Optical Network Unit (ONU)
Optical Network Unit (ONU)
 Optical Zoom
Optical Zoom
 OS Compatibility
OS Compatibility
 OSS Camera Lens
OSS Camera Lens
 OTG
OTG
 Outgoing Bandwidth
Outgoing Bandwidth
 Output Tray
Output Tray
 Over Current Protection (OCP)
Over Current Protection (OCP)
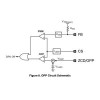 Over Power Protection (OPP)
Over Power Protection (OPP)
 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
 Over-Ear Headphone
Over-Ear Headphone
 Overclocking
Overclocking
 PA System
PA System
 PAL/NTSC
PAL/NTSC
 Panoramic
Panoramic
 Paper Feeder
Paper Feeder
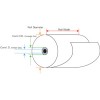 Paper Roll Core Inner Diameter
Paper Roll Core Inner Diameter
 Paper Roll Diameter
Paper Roll Diameter
 Paper Shredder
Paper Shredder
 Paper Thickness
Paper Thickness
 Patch Cord
Patch Cord
 PCI-Express Extension Cable
PCI-Express Extension Cable
 PCIe
PCIe
 PCIe Gaming Sound Card
PCIe Gaming Sound Card
 PDF
PDF
 Peak Current
Peak Current
 Pen Pressure Level
Pen Pressure Level
 PFC
PFC
 Photocopier
Photocopier
 Pico Digital Platform
Pico Digital Platform
 Playback (bit)
Playback (bit)
 Plug & Play
Plug & Play
 PNG
PNG
 Podcast
Podcast
 PoE
PoE
 PoE+
PoE+
 Polar Patterns
Polar Patterns
 Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate
 PON
PON
 Portrait
Portrait
 POS Printer
POS Printer
 Power Strip
Power Strip
 PP Soft Armrest
PP Soft Armrest
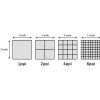 PPI
PPI
 PPM
PPM
 Prime Lens
Prime Lens
 Print Head
Print Head
 Print Margins
Print Margins
 Print Resolution
Print Resolution
 Print Speed
Print Speed
 Printing Calculator
Printing Calculator
 Privacy Shutter
Privacy Shutter
 Processor Base Frequency
Processor Base Frequency
 Processor Core
Processor Core
 Processor Thread
Processor Thread
 Processor Turbo Frequency
Processor Turbo Frequency
 Programmable Keys
Programmable Keys
 Projector
Projector
 Propeller
Propeller
 Proximity
Proximity
 PS +Metal (Material)
PS +Metal (Material)
 PU
PU
 PVC and PVC Composite
PVC and PVC Composite
 PWM Control
PWM Control
 RADF
RADF
 Raid of Server
Raid of Server
 RAM
RAM
 Ram Module Size
Ram Module Size
 Ram Performance Profile
Ram Performance Profile
 Random Read IOPS
Random Read IOPS
 Random Write IOPS
Random Write IOPS
 Range Extender
Range Extender
 Rapid IPS
Rapid IPS
 Rapid VA
Rapid VA
 Rated Current
Rated Current
 Rated Power
Rated Power
 RCA Port
RCA Port
 Rechargeable Battery
Rechargeable Battery
 Recording (bit)
Recording (bit)
 Red Dial Wheel
Red Dial Wheel
 Red-Eye Reduction
Red-Eye Reduction
 Red/Blue Switches
Red/Blue Switches
 Redial Memory
Redial Memory
 Refresh Rate (Hz)
Refresh Rate (Hz)
 Response Time (ms) 1ms (Gray to Gray)
Response Time (ms) 1ms (Gray to Gray)
 Retina Display
Retina Display
 RFID Card
RFID Card
 RGB
RGB
 RGB Illumination
RGB Illumination
 Rhythms/Patterns
Rhythms/Patterns
 Ribbon
Ribbon
 RJ11
RJ11
 RJ45 Connector
RJ45 Connector
 RJ9
RJ9
 RMS/Channel (Watt)
RMS/Channel (Watt)
 RMS/Subwoofer (Watt)
RMS/Subwoofer (Watt)
 Roller Wheel
Roller Wheel
 Router
Router
 RPM
RPM
 RS-232
RS-232
 S.M.A.R.T Support
S.M.A.R.T Support
 Safe Box
Safe Box
 SATA
SATA
 SATA Port
SATA Port
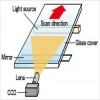 Scanning Method
Scanning Method
 Scientific Calculator
Scientific Calculator
 Screen Dots
Screen Dots
 SD/SDHC/SDXC
SD/SDHC/SDXC
 SDC VA
SDC VA
 SEC TFT VA
SEC TFT VA
 SEC VA
SEC VA
 Seek Time
Seek Time
 Sewing Machine
Sewing Machine
 Sewing Speed 750spm
Sewing Speed 750spm
 SFP
SFP
 SFP+
SFP+
 Shared Graphics Memory
Shared Graphics Memory
 Sheet Fed
Sheet Fed
 Shock Resistance
Shock Resistance
 Shock Sensor
Shock Sensor
 Shockproof
Shockproof
 Shockproof HDD/SSD
Shockproof HDD/SSD
 Short Circuit Protection (SCP)
Short Circuit Protection (SCP)
 Short Throw
Short Throw
 Shutter Speed
Shutter Speed
 Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
 Silica Gel (Material)
Silica Gel (Material)
 Single Function Printer
Single Function Printer
 Single Port Headphone
Single Port Headphone
 Single-Band
Single-Band
 Single-Player, Multiplayer
Single-Player, Multiplayer
 Single-Sided Card Printer
Single-Sided Card Printer
 SLI
SLI
 Smart Signage
Smart Signage
 Smart TV
Smart TV
 Smartwatch
Smartwatch
 Sound Card
Sound Card
 Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
 Soundbar
Soundbar
 Speed Class
Speed Class
 Speed Dialer
Speed Dialer
 Speed Rating of RAM
Speed Rating of RAM
 SpO2 Monitor
SpO2 Monitor
 SQL Server Standard
SQL Server Standard
 SS IPS
SS IPS
 Stacker Capacity
Stacker Capacity
 Standard Print Languages
Standard Print Languages
 Standard Throw
Standard Throw
 Static Pressure Air flow
Static Pressure Air flow
 Stereo Calling
Stereo Calling
 Stereo Headphone
Stereo Headphone
 Stereo Headphone Jack
Stereo Headphone Jack
 Stereo Microphone
Stereo Microphone
 STM Camera Lens
STM Camera Lens
 Storage Humidity
Storage Humidity
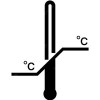 Storage Temperature
Storage Temperature
 Stylus Pen
Stylus Pen
 Surge Protector
Surge Protector
 Sweep Panorama
Sweep Panorama
 Tabletop Mode
Tabletop Mode
 Tarnish Resistant
Tarnish Resistant
 TDP
TDP
 Telescopic Selfie Stick
Telescopic Selfie Stick
 Temperature Proof
Temperature Proof
 Textured Surface
Textured Surface
 TF Card
TF Card
 TFT LCD
TFT LCD
 Thermal Conductivity
Thermal Conductivity
 Thermal Paper
Thermal Paper
 Thermal Solution (PIB)
Thermal Solution (PIB)
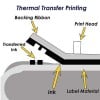 Thermal Transfer
Thermal Transfer
 Thread Tension Control
Thread Tension Control
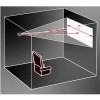 Throw Ratio
Throw Ratio
 Thunderbolt Port
Thunderbolt Port
 Tilt Angle
Tilt Angle
 TN Panel Type
TN Panel Type
 Toner
Toner
 Toslink Port
Toslink Port
 Total Security
Total Security
 TPM
TPM
 TPS
TPS
 TPU (material)
TPU (material)
 Transfer Key
Transfer Key
 Transmission Speed (spp)
Transmission Speed (spp)
 Tri Band
Tri Band
 Tri-Color
Tri-Color
 TRIM Support
TRIM Support
 Tripod
Tripod
 TRS
TRS
 Tuner Bands
Tuner Bands
 Turret CC Camera
Turret CC Camera
 TV Card
TV Card
 TV Streaming Device
TV Streaming Device
 TV Tuner Stick
TV Tuner Stick
 TWAIN
TWAIN
 Two-Way Audio
Two-Way Audio
 TWS
TWS